In today's automated logistics systems, particularly in industries like automotive manufacturing and warehouse operations, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have become a critical tool. AGVs are designed to improve efficiency, reduce human labor, and optimize the transportation of materials. One essential component that enhances AGV performance is the steering wheel, also known as the steering drive wheel. This unique component integrates the drive motor, steering motor, gearbox, and additional features into one compact unit, enabling AGVs to achieve both driving and steering capabilities with high efficiency.
1. Introduction to AGV Steering Wheels
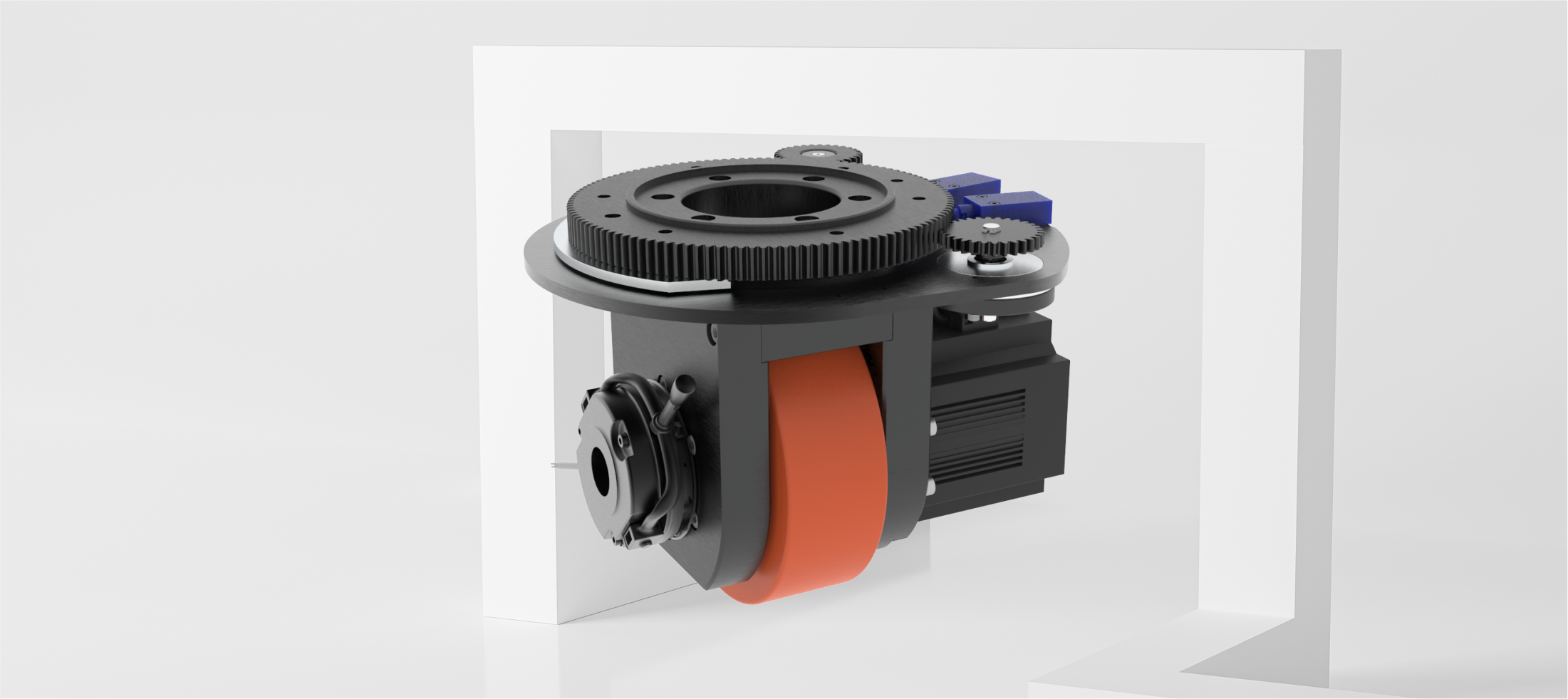
The term “steering wheel” refers to a component that combines several essential functions into one system, including driving, steering, and towing capabilities. This all-in-one mechanism allows AGVs to carry and tow heavy loads efficiently. Unlike traditional differential drive AGVs, which use separate components for movement and steering, the steering wheel offers a much higher level of integration, which makes it a versatile and effective solution. When paired with a servo system, it provides higher precision and faster response times, making it the ideal choice for modern AGVs in a variety of applications.
2. Components of the Steering Wheel
An AGV steering wheel is made up of several key components that work together to deliver both movement and steering capabilities:
-
Drive Mechanism: Typically, a DC motor is paired with a gearbox to provide the required driving force. The anti-symmetric installation of the motor ensures that the drive wheels are aligned, allowing for a compact AGV design without sacrificing power.
-
Key Features:
-
Compact size: The integrated design makes the steering wheel lightweight and small, which helps reduce the overall size of the AGV.
-
Easy operation: The system comes with an automatic centering feature for smooth handling.
-
High adaptability: Core components are equipped with shockproof systems to prevent damage from unexpected shocks during transport or operation.
-
Versatility: Available in both horizontal and vertical configurations, the steering wheel can be powered by either AC or DC sources. DC power is more stable and easier to control, while horizontal steering wheels are more compact but tend to be more expensive.
-
3. Types of Steering Wheels
AGV steering wheels come in two main configurations based on the orientation of the motor: horizontal and vertical.
-
Horizontal Steering Wheel: The motor is mounted horizontally, which results in a lower overall height. This design is ideal for AGVs that need to operate in low-clearance environments, such as those used in under-floor applications.

-
Vertical Steering Wheel: The motor is mounted vertically, offering a higher profile. This configuration is better suited for applications that require motor isolation for safety, such as in hazardous environments where explosion-proof features are needed.

Both types of steering wheels are equipped with high-power actuators for driving and low-power steering motors for precise control. The choice between horizontal and vertical steering wheels depends on the application’s space requirements and safety considerations.
4. Steering Wheel Chassis and Movement
The chassis design of an AGV plays a crucial role in determining the vehicle's driving and steering capabilities. The steering wheel enables AGVs to achieve omnidirectional movement by providing both traction and active steering. With one or more steering wheels, AGVs can move in any direction: forward, backward, sideways, or even rotate in place.
The precision of the steering wheel’s movement directly affects the AGV’s repeat positioning accuracy, which is vital for high-precision tasks in logistics and manufacturing environments. Typically, the wheels are made from polyurethane for optimal grip and durability, especially in indoor environments with smooth floors.
5. Steering Wheel Drive Systems
AGVs typically use three types of steering wheel configurations: single steering wheel, double steering wheel, and four steering wheels. These configurations allow for various levels of maneuverability and complexity:
-
Single Steering Wheel: This is a simpler configuration where the AGV is driven by a single wheel. It’s cost-effective and easy to control, but the range of movement is limited, and the vehicle's ability to change directions is basic.

-
Double Steering Wheel: With two steering wheels, the AGV can adjust its steering angle and speed, allowing for more complex movements, such as lane changes and turning in tight spaces. This setup offers greater flexibility and maneuverability, but it requires more precise control and coordination between the motors.

-
Four Steering Wheel: In this configuration, each wheel is equipped with its own motor for both driving and steering. This setup enables full omnidirectional movement, which means the AGV can move forward, backward, and side-to-side, even in very tight spaces. The four-steering wheel system offers the greatest flexibility but also introduces more complexity in terms of control and cost.

6. Steering Wheel Control and Coordination
The AGV control system relies on sensors to gather data about both the environment and the AGV's current status. The system uses this data to generate commands that adjust the servo motors, controlling the steering wheel to ensure the AGV follows its intended path.
By maintaining synchronized movements between the steering wheels, the AGV can perform a range of actions, including turning, reversing, and rotating in place. Coordinated control of the steering wheel is essential for ensuring the AGV performs these movements smoothly and efficiently, especially in complex environments with tight spaces and dynamic obstacles.
Conclusion: The Future of AGV Steering Wheel Technology
The AGV steering wheel is a pivotal component in the evolution of automated logistics systems. By combining drivingand steering functions into a single, integrated unit, the steering wheel significantly enhances AGV maneuverability, efficiency, and flexibility. Whether used in automotive manufacturing, warehouse logistics, or other industries, steering wheels enable AGVs to perform tasks with higher precision and greater speed. As automation technology continues to advance, the steering wheel will play an even more important role in improving the performance of AGVs and optimizing logistics processes globally.
Share:
Importance of AGV Motor Torque Calculation in AGVs for Automotive Manufacturing Logistics
AGV/AMR Design Calculator: Key Points from Parameter Calculations to Selection Guidelines